Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex works on pyruvate to produce Acetyl-CoA.
The requirements are: pyruvate, SH-Coa, NAD+
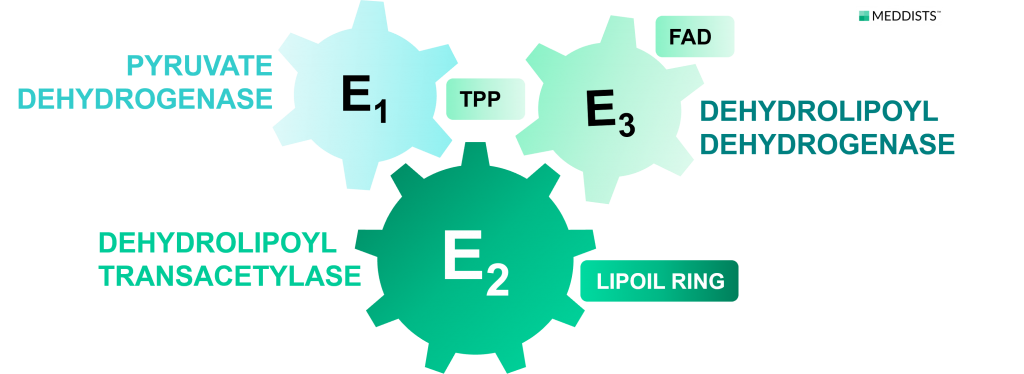
Cofactors of the complex: E1-TPP, E2-LIPOYL RING, E3-FAD
The pyruvate dehydrogenase enzyme complex (PDH)
The three main components — fatty acids, amino acids, and carbohydrates, can all be transformed into Acetyl-CoA.
When glucose is converted into pyruvate the pyruvate dehydrogenase enzyme complex (PDH) will form Acetyl-CoA. The enzyme complex in which three components are found, participating in the production of Acetyl-CoA (Figure 1):
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase (E1)
- Dehydrolipoyl transacetylase (E2)
- Dehydrolipoyl dehydrogenase (E3)
Functions
- The first enzyme will grab the pyruvate and take the hydrogen away (dehydrogenase activity)
- The second one changes the structures of this lipoyl ring (transacetylation activity)
- The third one will “play” with hydrogen — (dehydrogenase activity)
If we take the hydrogen, we need an acceptor molecule for it, and
