Goes until cells are capable to take up the mono forms (glucose)
D-type of sugar is used by our body
GLUT transmembrane proteins are responsible for the uptake
the uptake is ATP and Sodium-potassium co-transport dependent
GLUT5 is for fructose with facilitated diffusion
GLUT4 is insulin-dependent
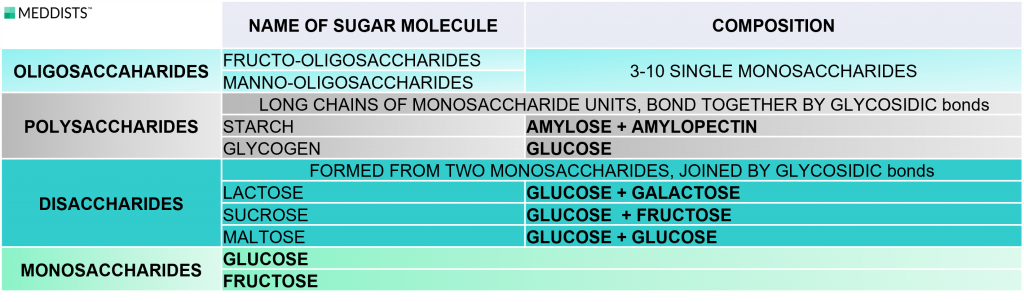
Digestion and absorption of food carbohydrates
Between carbohydrates, we are considering complex forms like
- oligo- and polysaccharides
- disaccharides and
single forms, like the - monosaccharides
As a result of enzymes in the gastrointestinal tract, the polysaccharides are decomposed into monosaccharides because they can only be absorbed in the monosaccharides form through the small intestinal cells (Figure 1).
As a first step in the mouth, the alpha-amylase produced in the salivary glands hydrolyses alpha-1-4 bonds, thus disrupts starch and glycogen, but inactivates by the acidic pH of the stomach.
The pancreatic alpha-amylase produced by the
