In females, the breasts form the secondary sexual features, providing nutrition for the newborn.
Location
- The breasts lie within the superficial fascia
- The base extends from the 2nd-3rd to the 6th rib, and in the transverse plane from the sternal edge medially almost to the midaxillary line laterally
A small process extends from the breast towards the axillary fossa called the axillary tail or the tail of Spence.
Description
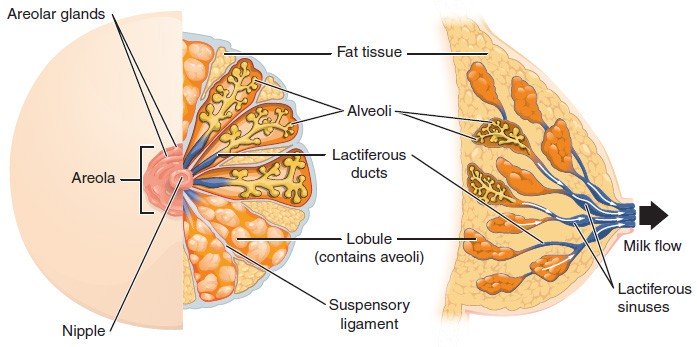
- The greatest prominence of the surface of the breast is the nipple, surrounded by a circular pigmented area of skin, the areola
- The nipple is the opening of the lactiferous sinuses for the ejection of breast milk
- The most important constituents of the breasts are the mammary glands which are located in the subcutaneous tissue
- There are 3 other types of glands that can be found in the breasts:
- Sweat glands
- Sebaceous glands
- Montgomery glands — Provide protection to the nipple
- The initial breast milk is
- There are 3 other types of glands that can be found in the breasts:
