The chambers of the heart consist of the two atria and the two ventricles.
- The atria are separated from the ventricles by the coronary sulcus (atrioventricular sulcus) externally
- The two ventricles are separated from each other by the interventricular sulci (anterior and posterior)
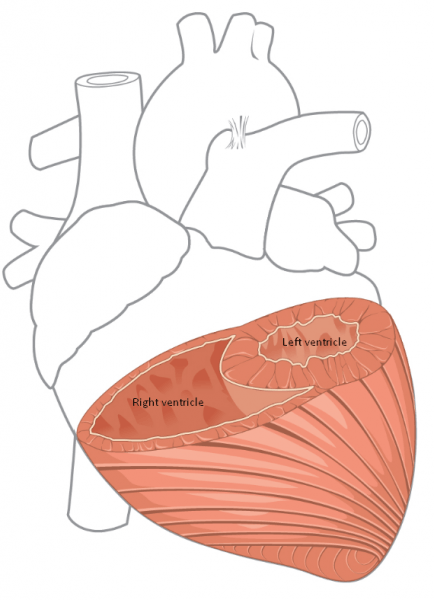
- The wall of the left ventricle is much thicker than the right — up to 3 times more — 10-12mm vs 3-4mm
Right atrium
- The right atrium receives blood from two large veins, Inferior and Superior vena cava
- The blood flowing into the right atrium is considered as deoxygenated blood (venous blood)
- During the diastolic phase, blood entering from the right atrium into the right ventricle via the atrioventricular orifice — the Tricuspid valve
Landmarks
- The valve of the inferior vena cava (Eustachian valve)
- The valve of the coronary sinus (Thebasian valve)
- Tendon of Todaro (the joining point of the two
