The trigeminal nerve provides innervation to the face and meninges, and supplies motor innervation to the masticatory muscles. It divides into three parts as it originates: ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular.
Divisions
The trigeminal nerve is divided into three divisions (also known as V1,2,3):
These divisions provide distinct areas of sensory innervation, and the mandibular division provides motor innervation as well, for the masticatory muscles.
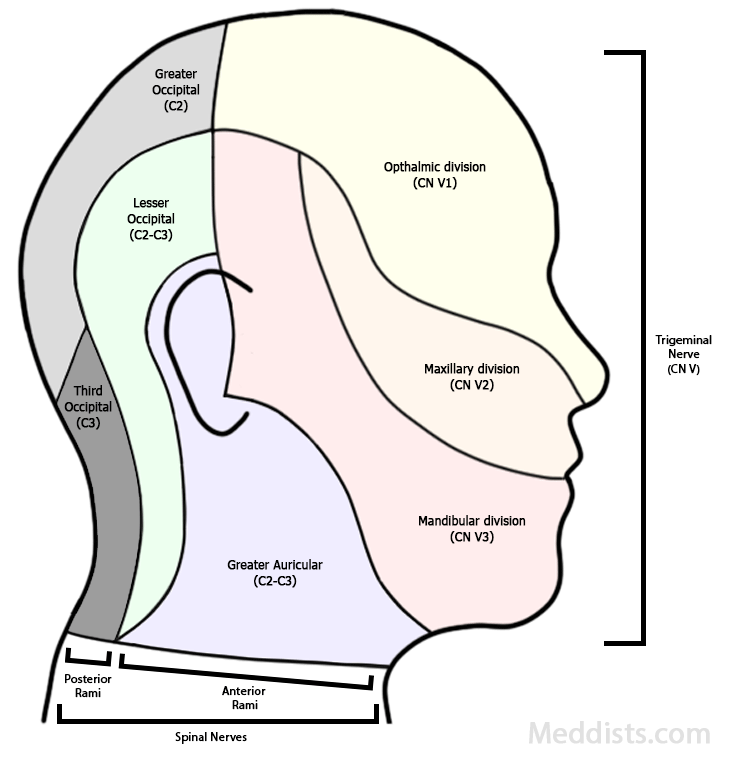
Opthalmic division
The ophthalmic division exits through the superior orbital fissure. It provides sensory innervation to the anterior scalp, forehead, orbital regions, upper nose, and inside the nasal cavity.
Its main branches include:
- Tentorial nerve
- Nasociliary nerve
- Long ciliary nerve
- Short ciliary nerve
- Anterior ethmoidal nerve
- Posterior ethmoidal nerve
- Infratrochlear nerve
- Frontal nerve
- Supra-orbital nerve
- Supratrochlear nerve
- Lacrimal nerve
- The anterior and posterior ethmoidal nerves innervate the nasal cavity.
- The supra-orbital nerve innervates the middle
