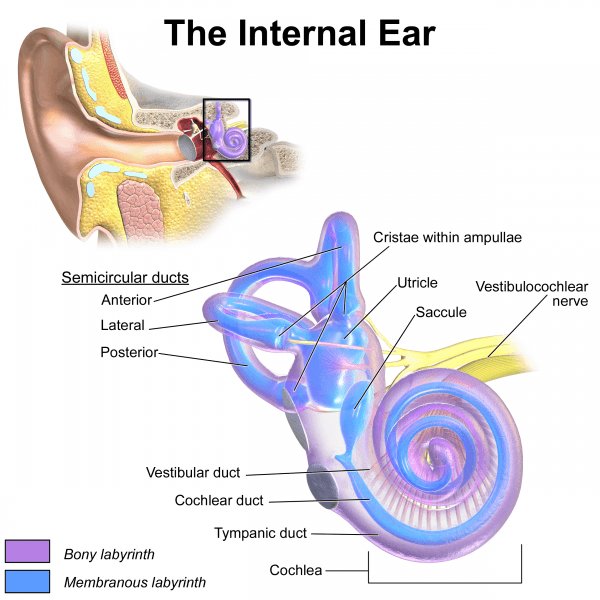
Description
The inner ear is composed of an outer wall -- the bony labyrinth, which forms a hollow and continuous system of tubes and sacs lined by a membranous labyrinth.
The membranous labyrinth is regarded as the actual system of organs of sound and balance, while the bony labyrinth is the other shell.
Inner ear spaces
Within the inner ear there are three fluid-filled spaces, named in regard to the membranous labyrinth:
- Endolymphatic space
- Perilymphatic space
- Cortilymphatic space
Endolymphatic space
The innermost space, located within the membranous labyrinth.
The fluid within this space is called endolymph, and it has a similar composition to intracellular fluid -- high K+ and low Na+ concentrations.
Perilymphatic space
Located
