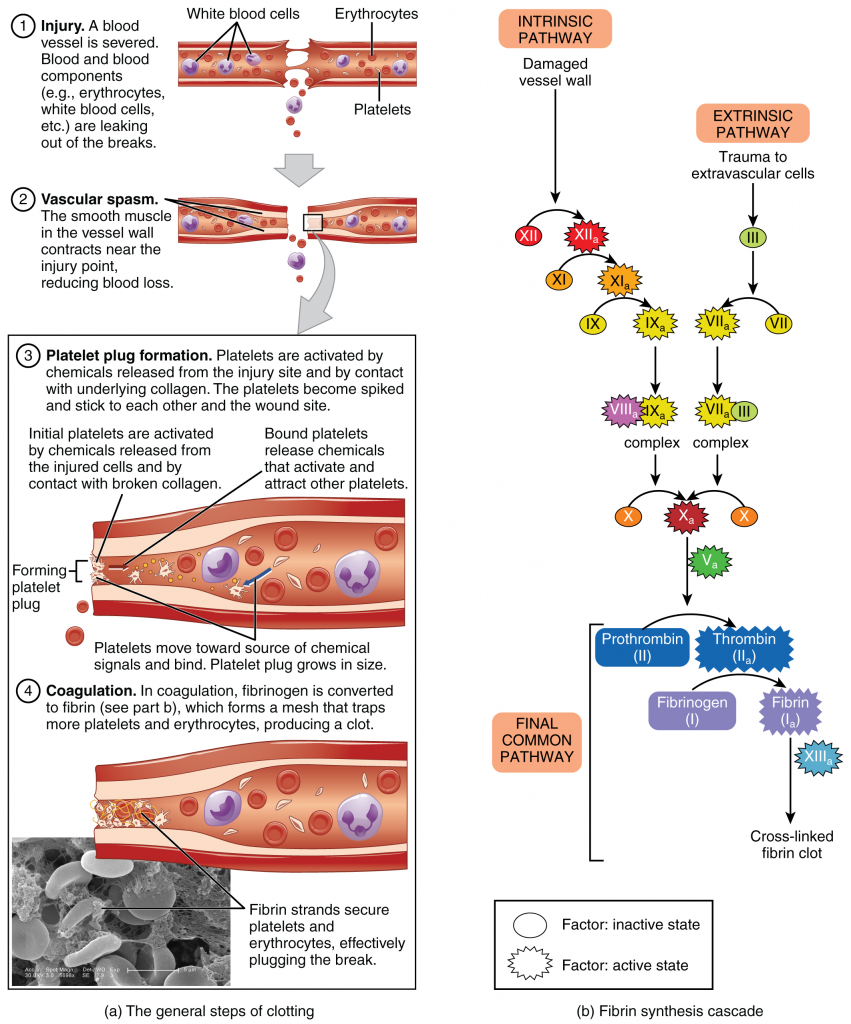
Hemostasis refers to the process by which bleeding is stopped.
It consists of three main stages:
- Local vasoconstriction
- Formation of a platelet plug
- Blood coagulation (clotting)
Description
Generally, hemostasis is divided into three distinct stages:
- Local vasoconstriction: vasospasm
- Primary hemostasis: platelet activation
- Secondary hemostasis: clot formation
Local vasoconstriction
Once a blood vessel is injured, an immediate response to the injury involves local vasoconstriction to reduce blood flow and a subsequent blood loss from the site of injury.
The vasoconstriction is primarily mediated by endothelin-1, a potent vasoconstrictor, which is synthesized by the damaged endothelium.
Formation of a platelet plug
Platelets circulate through the blood and become activated once they reach a site of vascular injury.
- Their main functions include:
- Adhesion
- Aggregation
- Release mediators
- They carry numerous receptors:
- Collagen
